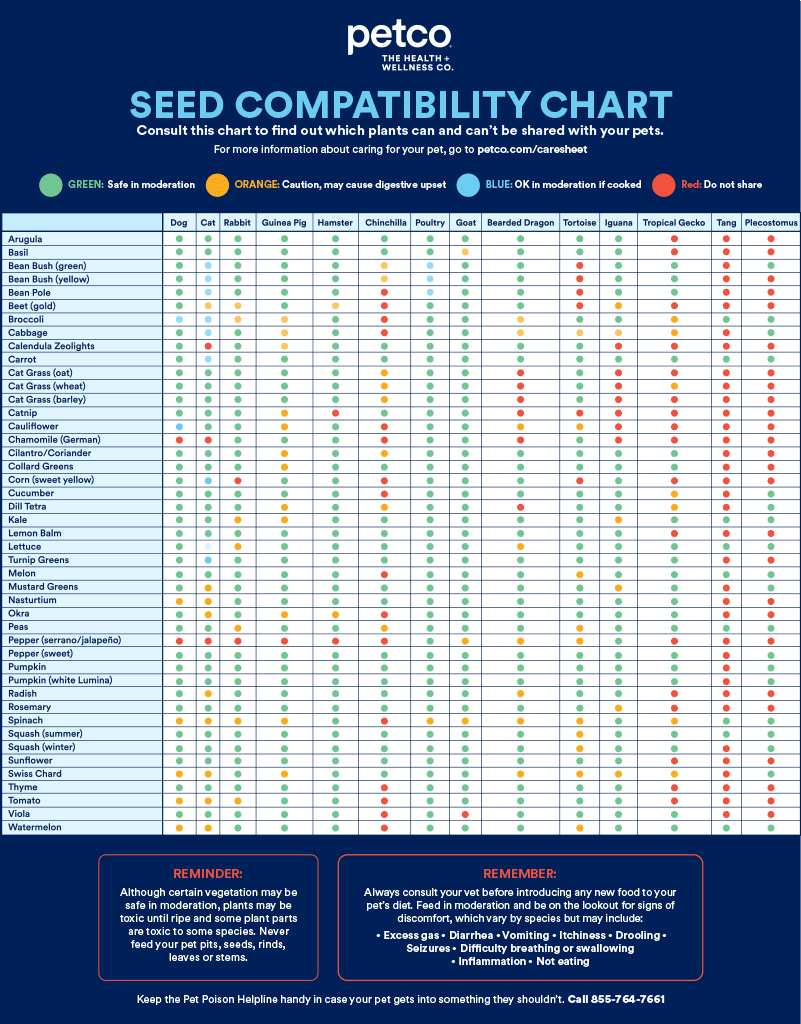
How to Check Bearded Dragon Gender
Updated On April 22nd, 2025

You might look at this title and think to yourself, “Well, that shouldn’t be too complicated,” but in reality, there are many different ways to differentiate between bearded dragon sexes. Though the approach to caring for female and male bearded dragons remains the same, it’s still helpful to know the sex of your beardie. Let’s start with the basics.
There are several ways you can determine if your pet is a male or a female bearded dragon, and some methods are easier than others. While an experienced hobbyist may be able to determine gender early on, many pet parents tend to find success once the bearded dragon is 4-6 months or older. Beardies older than 12 months are the most straightforward, but .there are also safe and effective ways of determining a young beardie’s sex.
How to determine the sex of a bearded dragon
“Is my bearded dragon male or female?” might be one of the first questions you ask about your new beardie pet. Generally speaking, the older your bearded dragon is, the easier it will be to determine their sex. Adult beardies have features that baby bearded dragons have not fully developed yet.
For the best understanding of how to determine the gender of bearded dragon pets, try these five methods:
1. Check for hemipenal bulges
The fastest and easiest way to determine the bearded dragon’s sex is by looking for what are called hemipenal bulges. These bulges indicate the presence of hemipenes, which are the male bearded dragon’s internal sex organs. This is the quickest technique for beardies 4-6+ months old.
Hemipenal bulges are found on the underside of your bearded dragon, towards the back of their tail. If you have recently brought your reptile home, wait until you’re both comfortable with each other before handling them in this way. Once you’re both ready, here’s what you need to do to check:
- Rest them on a solid, sturdy surface or pick them up applying gentle pressure to their thoracic region underneath the bearded dragon as well as on top of the shoulder blades using your thumb. Support all 4 legs between your fingers and the palm of your hand or rest the body along your forearm.
- With your other hand, gently lift the caudal base of their tail upwards into an angled position not to exceed 90 degrees. Never grab the tip of the tail, as you can more easily cause damage or break the tip of tail. By lifting up the tail, the base of the tail will stretch around the sex glandsmaking gender identification easier.
- Look for an outline of the hemipenal bulges or lack thereof.
Male bearded dragons have two defined grooves running vertically down the tail to the cloacal opening, whereas female bearded dragons have one single vertical bulge above the cloacal opening in the center which is smoother and not as visible as a male’s.
Depending on the bearded dragon, it may be hard to see at first. If you can’t see the bumps, lift the tail a little more to stretch the skin and make the hemipenal bulges, if present, more noticeable. Take care not to lift their tail too high or too far back, as this could cause your beardie discomfort.
2. The flashlight method
This is essentially the same method as above, but it involves using a small flashlight. Shining a flashlight from the top of the bearded dragon through the base of the tail will make their sex organs much easier to see. This method is also better for determining the sex of baby bearded dragons.
- Start by following the process outlined in Step 1 above to place the bearded dragon on a solid surface or pick them up correctly using one hand
- With your other hand, shine a flashlight on the upper side at the base of the tail and lift, not to exceed 90 degrees. Be sure the small flashlight is placed at the base of the tail right where the tail meets the body.
- Looking from the back of your bearded dragon’s tail, you should see the base of the tail glow slightly red in a dark room with one or two dark shadows within the base of the tail, indicating the location of the bulges.
Male beardies will have two shadowed or dark bulges, while females will only have one in the center and the rest of the base of the tail should glow red.
3. Femoral pores and size
Another way of determining the bearded dragon sexes is by looking at their femoral pores. Bearded dragons use femoral pores to secrete pheromones. They are found on the underside of your beardie’s back legs. Healthy bearded dragon pores look like small circles running across their thighs.
Male bearded dragons have much larger femoral pores than females. They’re also more distinct and pronounced. There is no set way to measure the femoral pore size of male vs. female bearded dragons due to their small size, but it is very clear to see which are larger if you have the ability to compare two different genders side by side.
It’s also important to note that femoral pores only fully develop when a bearded dragon reaches adulthood. If your beardie is less than 12 months old, you might not get accurate results using this method.
4. Watch their behavior
Watching for specific behaviors of bearded dragon sexes may help you when sexing a bearded dragon. Males and females have very different behaviors.
Males show aggressive and dominant behaviors such as hissing and stomping. Males also bob their heads more and fluff their beards. Beard fluffing is used to make them seem bigger and more threatening.
Despite the fact that these behaviors are more common in males, these behaviors can also be shown by females. For this reason, using a bearded dragon’s behavior to determine their sex is the least accurate method. It also needs close observation and skilled judgment.
5. The cloacal opening
The cloacal opening is also known as a vent. It is found on the underside of a bearded dragon between its rear legs and is the opening used to pass feces, urate and eggs. Males have a wider cloacal opening than females.
How to determine the sex of a baby bearded dragon
It can be difficult to determine the gender of a baby bearded dragon. Sexing babies and juveniles will not be as accurate as sexing adults. This is because the features used to identify their gender have not fully developed yet. If you want to be 100% certain about their sex, it’s best to wait to try the aforementioned strategies until they are at least 12 months old.
To sex a baby bearded dragon, it is generally best to wait a minimum of 8-12 weeks and start by using the flashlight technique described above. You can then try and confirm your guess by looking at their tail.
Females’ tails are narrow and taper sharply at the base. Males have slightly thicker tails towards the base. These differences become more pronounced and easier to identify as they grow. Some suggest you can also look at their head size. It is true that males have a wider skull, but this is not easy to observe in babies and should be avoided.
What is the difference between male and female bearded dragons?
Adult bearded dragons are sexually dimorphic, meaning the male and female physically differ from each other. Males have two hemipenal bulges, enlarged femoral pores, bigger heads, thicker tails and darker beards when compared with females. All these differences can be seen in adult individuals by using the sexing steps listed above. You may also notice differences in male vs. female behaviors and the presentation of spikes.
Some of the easiest ways to spot the difference between males vs. females include:
Head size
Bearded dragon head shape and size are different between males and females. Male bearded dragons usually have larger and thicker heads. Females have a thinner skull and smaller heads.
Tail size
Males and females also have slight differences in their tails. If you drew a bearded dragon outline of a male and female body, you would notice that males have thicker tails at the base. A female’s tail is much narrower and more slender. If you are trying to use a bearded dragon’s tail to sex them, wait until 12 months of age.
Aggressive and Submissive Behaviors
Male bearded dragons are more protective and can show territorial aggression. This can be seen through hissing, stomping, beard fluffing and head bobbing. Males are also more likely to have dark beards. Females are more likely to show submission through arm waving—especially juveniles.
Spikes
Male and female bearded dragons both have spikes around their beards, heads and throats. Spikes are used to protect bearded dragons by scaring off predators. Bearded dragons will puff their bodies—which stiffens the spikes—creating a more threatening appearance and defensive weapons. However, males and females use these spikes differently:
- Males present their spikes when they are ready to mate.
- Females present their spikes when they are feeling threatened. They are more likely to wave their arms when ready to mate.
Remember, identifying all the differences between males and females requires experience. Differences between males and females are not always easy to spot, and behaviors can be shown by both sexes for different reasons.
Whether you have a male or female bearded dragon, you’ll want to have the best supplies and solutions to help them live their best life. At Petco, you can find bearded dragon tanks and terrariums for your beardie to call home. Check out bearded dragon décor to fill your tank with and bearded dragon heating and lighting equipment to set up an appropriate environment. Plus, you’ll find all the bearded dragon health and wellness solutions you need, including supplements, vitamins and more.
Related Articles
Related Questions

Sponsored
Two Easy Ways to Start Earning Rewards!
Become a member today!Members-only pricing and offers, personalized care notifications, Vital Care points back on every purchase and more!Become a credit card member today!
Earn 2X Pals Rewards points at Petco
when you use Petco Pay!APPLY NOWLearn More About Petco Pay Benefits